DevOps AWS Course
Duration: 3 Months – 120 Total hours
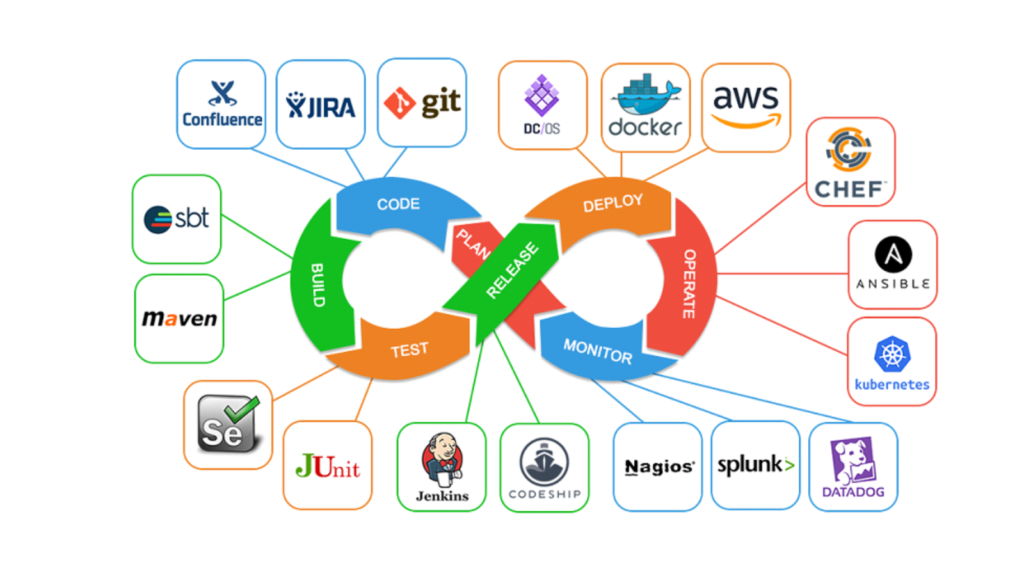
Course Content:
SECTION 1 – Introduction to DevOps
- What is DevOps?
- Why DevOps?
- Benefits of DevOps
- Overview of DevOps
SECTION 2 – Software Version Control
- Basics of Software Version Control
- Complete concepts in Version Control Systems
- Study about SCM, Command Line, GIT.
SECTION 3 – GIT Introduction & Installation
- GIT Quick Start
- Installation and setup
- Installation and setup
- Branching & Merging in GIT
- GIT Rebase, Stashing, Tagging
- Version Control System GIT with GITHUB
SECTION 4 – Automation Build and Test
- Basics about the Automating Builds – Maven, Ant
- Installing the required tools Ant, Maven, Jenkins.
- DevOps Test Automation tools and framework
SECTION 5 – Continuous Integration (CI)
- Study about DevOps Continuous Integration
- DevOps Continuous Integration Tools Comparison
- Overview of Jenkins Pipeline
- DevOps Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
- DevOps Continuous Integration Pipeline, Jenkins, Testing
- Benefits of DevOps Continuous Integration
- Jenkins as a Code Pipeline (DSL)
- Distributed Builds in Jenkins (Master and Slave)
- Parameterize Jenkins Jobs
- Jenkins Security Aspects
SECTION 6 – Linux Basics and Shell scripting
- Introduction to Linux Basics
- Creating and executing Bash scripts
- Scheduling Bash scripts in Crontab
SECTION 7 – Containerization with Docker
- What are Containers?
- Difference between VM and Container, Docker Fundamentals
- Docker Setup and Installation on windows/Linux Machine
- Docker Basics & Run Container
- Docker File Basics | Introduction
- Build and Tag Project Docker Image
- Creating & Running Docker containers using Image Distribution.
- Create Custom Docker Image and push it to docker hub.
- Docker Compose: Multi Container Tool
- Docker Swarm Orchestration features and Applications.
- Networking Concepts in Docker
- Using a Docker volume
SECTION 8 – Container Orchestration with Kubernetes
- Introduction to Kubernetes, the cluster architecture of Kubernetes
- Creating a Kubernetes cluster on AWS
- What is YAML, creating YAML with Kubernetes deployment
- Micro Services in Kubernetes
SECTION 9 – Chef
- Chef fundamentals, Chef Environment and architecture
- Chef cookbooks & Knife Commands
- Introduction to Ruby DSL Scripts
- Deploying Nodes in Production and using the open source chef hosted server.
SECTION 10 – Ansible
- Introduction to Ansible.
- Configuration, Writing Ansible Playbooks
- Introduction to YAML Scripts
- Ansible Based Configuration Management
- Different Roles
- Command Line usage
SECTION 11 – Nagios Performance and Automation Monitoring
- What is Nagios?
- DevOps monitoring with Nagios
- Features of Nagios
- Nagios Architecture
- Configuring Nagios in Monitoring Webserver for Services, Objects and Notifications.
SECTION 12 – Cloud Computing
- Introduction to Cloud
- Cloud features: Elasticity, Pay as you use,
- Different models of Cloud: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
- Creating AWS account
- Free tier Eligible services
- Understanding AWS Regions and availability zones
- EC2 (Elastic Cloud Compute)
- About EC2 and types, Pricing
- Launch windows and Linux Instances in AWS
- Connecting windows and Linux instances from windows desktop and Linux machines
- About AWS Storage services, EBS, and S3
- Creating S3 Buckets and putting objects in a bucket
- Discussion about Bucket Properties
- S3 Pricing
- About S3 glacier
- EBS (Elastic Block Storage)
- Types of EBS Volumes
- Creation, attaching and detaching volumes
- ELB (Elastic Load Balancer)
- Understanding the load balancing o Configuring ELB and adding the webservers under ELB
- Auto Scaling
- Types of Scaling (Horizontal and Vertical)
- Configuring Launch Configuration
- Creating and defining the auto scaling group policy
- IAM (Identity Access Management)
- Understanding of AWS Security using IAM
- Definition of Roles, policies and Groups
- Creating IAM Users and managing password policies
SECTION 13 – Terraform
- Provisioning Infrastructure
- Modify existing resources.
- Destroy Infrastructure
- How to completely destroy the Terraform-managed infrastructure.
- Parameterize your configuration with input/output variables.
- Organize your data for easier queries with outputs.
- Modules
- Refactor your existing configuration into a module for reusability.
